Biomedical engineer in robotics, diagnostic imaging and telemedicine
Description
The biomedical engineer in health technology gathers mainly knowledge about engineering, medicine and also basic knowledge of physics, chemistry and biology. He can work in three professional fields: industry, healthcare and research and he/she is the link between medicine and engineering, He/she must understand what a physician asks him to be able to define the specifications the product must have. He also manages projects and can handle manufacturing, evaluation, certification, marketing, maintenance, calibration, repair and training in the use of new widgets and instruments.
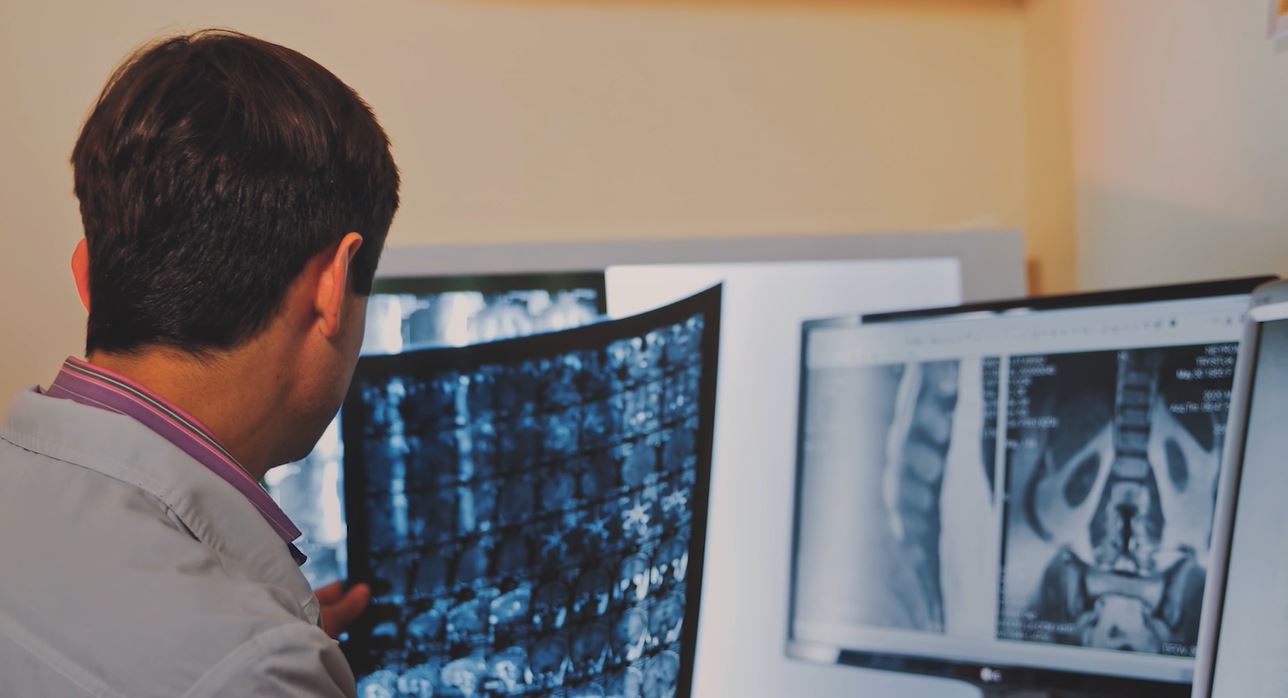
His work can be developed in various fields: implants and biomaterials, medical instrumentation, therapeutic and preventive diagnostic systems, medical signal processing, devices for the disabled, radiation applications in medicine, diagnostic imaging and medical robotics for surgical interventions.
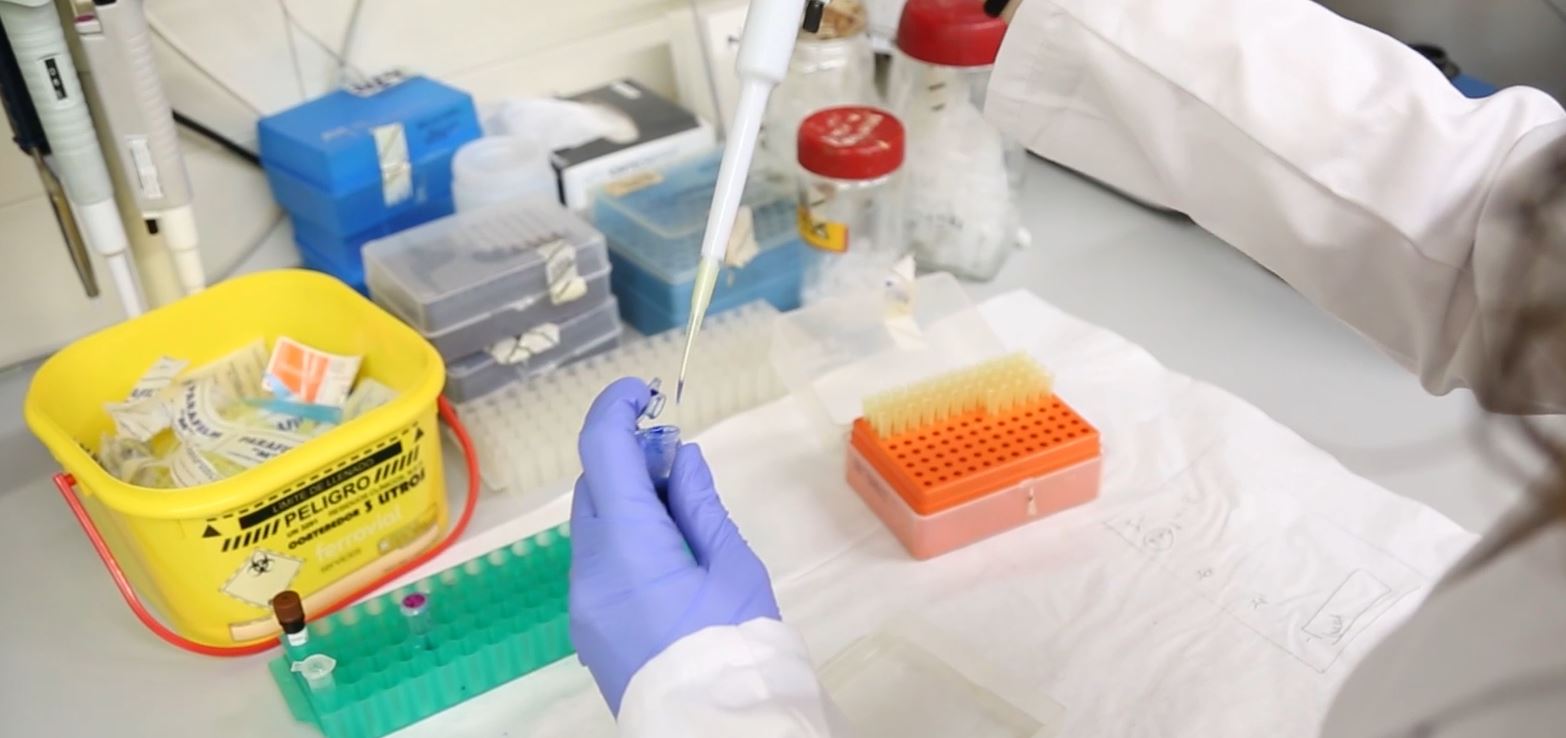
This professional uses portable diagnostic platforms and control devices, using the tools and technologies of bioengineering to better understand the behavior of proteins, cells, tissues and body organs, or to design solutions such as nanocapsules for the targeted administration of drugs, nanoedins for the study of biological systems, molecular actuators that can be switched with light and in vitro organs ¿on a chip¿ for disease models. It also studies the mechanisms and physiological implications that underpin mechanical forces in biology, such as the mechanical behavior of cells and their interactions with the microenvironment, or the dynamic mechanisms involved in tissue healing, morphogenesis. and collective cell invasion in cancer.
The combination of new adaptable nanobiomaterials and cell engineering is leading to a number of advances in biomaterials that allow damaged or aged human tissues to be repaired and replaced. Tissue engineering involves the synthesis, processing, and characterization of new materials, such as polymers, proteins, crystals, cements, composites, and hybrids, with the goal of manufacturing materials that can be used as physical supports for manipulated tissues through engineering.
Signal processing development, sensors, data analysis, robotics and intelligent control systems are making possible remote care or assisted líving, and makes possible people affected by dementia or chronic diseases to live at home.
Tasks
- Design and planning development on research projects and resources management as human resources and time.
- Contacts the physician who needs a specific product, gathers information and defines project specifications accordingly to the providing company and the doctor.
- Create prototypes with which tests are performed and costs are analyzed.
- Produces and manages the required documentation for approval (legal approval by the competent administration) and marketing: user manuals, use instructions, prototype electromagnetic Compatibility and product definition.
- It is in charge of the final technical report .
- Look for instrument or apparatus supplier companies. It deals with the purchase of any kind of materials.
- Supervises and coordinates the repair, adaptation, maintenance and optimization of medical equipment and instruments.
- Can participate in studies on the interrelationships between physical systems and biological systems. For example, in the case of an artificial eye, microelectronic elements (cables, circuits) must be combined with other materials (plastics, metals) and biological molecules (rhodopsin) or nanobiology applications.










 | Catalan | Beginner
| Catalan | Beginner | Catalan | Advanced
| Catalan | Advanced
 Open
Open | English | Beginner
| English | Beginner